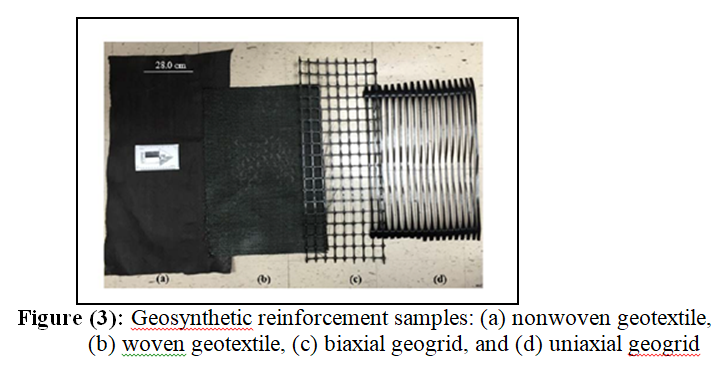
A Comprehensive Review of the Shear Performance of Recycled Pavement Materials Reinforced with Geogrids
Main Article Content
Abstract
Reuse of recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) has generated immense interest in pavement design because it stands out in terms of performance, economy, and the environment when compared to virgin aggregate. RAP is an eco-friendly alternative to natural aggregates, as about 97 percent of the material is recycled to form new pavement, and the remaining portion is used as foundation course material for the construction of roads. Researchers have looked at RAP's mechanical characteristics, including its stiffness, resilience modulus, and deformation behavior, in great detail. Its behavior in unbound layers is not always the same. Even though RAP has a lot of material and causes more permanent deformation, the research suggests that RAP-VA blends may have the same or even higher modulus and stability. RAP is useful right away, but it has also been shown to improve the performance and stability of subgrade and subbase courses in soils. Geogrids and other geosynthetics are two of the most significant components that improve the mechanical properties of RAP and other recycled materials. Geogrids promote load distribution, bearing capacity, and stiffness while decreasing rutting and settling via interlocking, shear transfer, and the tensioned membrane effect. They are mostly used to build tunnels, keep railways stable, make retaining walls, and make pavements. MSE walls are considered to be cost-effective, long-lasting, and a substitute for retaining walls and embankments. Some researchers have demonstrated improved interface shear strength and long-term performance in geogrid-RAP interaction. In this regard, geosynthetics and RAP are viable alternatives and offer a sustainable solution for new highway construction in a way that reduces raw material requirements and pavement infrastructure strength and durability.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Licensed under a CC-BY license: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
How to Cite
References
U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement in Asphalt Mixtures: State of the Practice, FHWA-HRT-11, 2011.
E. Rathje, A. Rauch, D. Trejo, K. Folliard, C. Viyanant, M. Esfellar, A. Jain, and M. Ogalla, Evaluation of Crushed Concrete and Recycled Asphalt Pavement as Backfill for Mechanically Stabilized Earth Walls, CTR Tech. Rep. 0-4177-3, 2006.
S. Magar, F. Xiao, D. Singh, and B. Showkat, “Applications of reclaimed asphalt pavement in India – a review,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 335, p. 130221, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130221.
B. K. Pandey, “Utilization of agricultural and industrial waste as replacement of cement in pavement quality concrete: A review,” Environmental Science and Pollution Research, vol. 29, pp. 24504–24546, 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-18189-5.
S. Debbarma and G. D. Ransinchung, “Achieving sustainability in roller compacted concrete pavement mixes using reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates state of the art review,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 262, p. 125078, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125078.
L. Yao, Z. Leng, J. Lan, R. Chen, and J. Jiang, “Environmental and economic assessment of collective recycling waste plastic and reclaimed asphalt pavement into pavement construction: A case study in Hong Kong,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 336, p. 130405, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130405.
S. K. Sahdeo, G. Ransinchung, K. L. Rahul, and S. Debbarma, “Reclaimed asphalt pavement as a substitution to natural coarse aggregate for the production of sustainable pervious concrete pavement mixes,” Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, vol. 33, p. 04020469, 2021, doi: 10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0003555.
M. Singh, A. Adhikari, M. K. Maurya, A. Srivastava, and R. S. Chhabra, “Feasibility study on use of washed-reclaimed asphalt as a partial replacement of natural aggregate in dry-lean concrete as base course for rigid pavement,” Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, vol. 32, p. 04020266, 2020, doi: 10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0003339.
S. Singh, G. D. Ransinchung, and P. Kumar, “An economical processing technique to improve RAP inclusive concrete properties,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. 148, pp. 734–747, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.030.
G. Guduru and K. K. Kuna, “Classification of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) material using simple indicative tests,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. 328, p. 127075, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127075.
C. Yang et al., “Performance characterization and enhancement mechanism of recycled asphalt mixtures involving high RAP content and steel slag,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 336, p. 130484, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130484.
T. Bennert, W. J. Papp, A. Maher, and N. Gucunski, “Utilization of construction and demolition debris under traffic-type loading in base and subbase application,” Transportation Research Record, vol. 1714, pp. 33–39, 2000.
Y. Song and P. S. K. Ooi, “Resilient modulus characteristics of varying percent of reclaimed asphalt pavement,” in Proc. GeoShanghai Int. Conf., Shanghai, China, Jun. 3–5, 2010, pp. 43–50.
E. McGarrah, Evaluation of Current Practices of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement/Virgin Aggregate as Base Course Material, Rep. No. WA-RD 713.1, Univ. of Washington, Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2007.
E. Noureldin and M. Abdelrahman, “Modeling of the resilient modulus for recycled asphalt pavement applications in base course layers,” Transportation Research Record, vol. 2371, pp. 121–132, 2013.
E. Hoppe, S. Lane, M. Fitch, and S. Shetty, Feasibility of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) Use as Road Base and Subbase Material, Rep. No. VCTIR 15-R6, Virginia Center for Transportation Innovation and Research, Univ. of Virginia, 2015.
K. Nokkaew, “Characterization of recycled aggregate for use as base course material,” International Journal of Geomate, vol. 15, pp. 129–136, 2018.
M. Arshad, “Development of a correlation between the resilient modulus and CBR value for granular blends containing natural aggregates and RAP/RCA materials,” Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 2019, p. 8238904, 2019.
W. Kim, J. F. Labuz, and S. Dai, “Resilient modulus of base course containing recycled asphalt pavement,” Transportation Research Record, vol. 2005, pp. 27–35, 2007.
T. B. Edil, J. M. Tinjum, and C. H. Benson, Recycled Unbound Materials, Rep. No. MN/RC 2012-35, Minnesota Dept. of Transportation, 2012.
M. Arshad and M. F. Ahmed, “Potential use of reclaimed asphalt pavement and recycled concrete aggregate in base/subbase layers of flexible pavements,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. 151, pp. 83–97, 2017.
S. Ullah, B. F. Tanyu, and E. J. Hoppe, “Optimizing the gradation of fine processed reclaimed asphalt pavement and aggregate blends for unbound base courses,” Transportation Research Record, vol. 2672, pp. 57–66, 2018.
S. Ullah and B. F. Tanyu, “Effect of variation in moisture content on the mechanical properties of base course constructed with RAP-VA blends,” in Proc. Geo-Congress 2020: Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering and Special Topics, Minneapolis, MN, USA, Feb. 25–28, 2020, pp. 612–620.
A. O. Al-Shujairi, A. J. Al-Taie, and H. M. Al-Mosawe, “Review on applications of RAP in civil engineering,” in Proc. 5th Sci. Conf. Eng. Postgraduate Res. (PEC 2020), vol. 1105, p. 012092, 2020.
C. Benson, J. Tinjum, and K. Nokkaew, “Hydraulic properties of recycled asphalt pavements and recycled concrete aggregate,” in Proc. GeoCongress, ASCE, 2012.
A. Suddeepong et al., “Polyethylene terephthalate modified asphalt concrete with blended recycled aggregates: Analysis and assessment,” Civil Engineering Journal (Iran), vol. 10, no. 11, pp. 3569–3588, 2024, doi: 10.28991/CEJ-2024-010-11-08.
A. H. Z. Chfat, H. Yaacob, N. M. Kamaruddin, Z. H. Al-Saffar, and R. P. Jaya, “Performance of asphalt mixtures modified with nano-eggshell powder,” Civil Engineering Journal, vol. 10, no. 11, pp. 3699–3720, 2024, doi: 10.28991/CEJ-2024-010-11-016.
M. Cubas, E. Correa, W. Benavides, R. Suclupe, and G. Arriola, “Modified asphalt mixtures incorporating pulverized recycled rubber and recycled asphalt pavement,” Civil Engineering Journal (Iran), vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 420–436, 2025, doi: 10.28991/CEJ-2025-011-02-02.
M. Tsakoumaki and C. Plati, “A critical overview of using reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) in road pavement construction,” Infrastructures, vol. 9, no. 8, p. 128, 2024, doi: 10.3390/infrastructures9080128.
G. Tarsi, P. Tataranni, and C. Sangiorgi, “The challenges of using reclaimed asphalt pavement for new asphalt mixtures: A review,” Materials, vol. 13, no. 18, p. 4052, 2020, doi: 10.3390/ma13184052.
Q. Dong and B. Huang, “Laboratory evaluation on resilient modulus and rate dependencies of RAP used as unbound base material,” Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, vol. 26, pp. 379–383, 2014.
E. Jeon, B. Steven, and J. T. Harvey, “Comprehensive laboratory testing and performance evaluation of recycled pulverized hot-mix asphalt material,” Transportation Research Record, vol. 2104, pp. 42–52, 2009.
S. K. Pradhan and G. Biswal, “Utilization of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) as granular sub-base material in road construction,” Materials Today: Proceedings, vol. 60, pp. 288–293, 2022.
M. Attia, Characterization of the Structural Behavior of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement as Pavement Base Layer, Ph.D. dissertation, North Dakota State Univ., Fargo, ND, USA, 2010.
R. Taha, G. Ali, A. Basma, and O. Al-Turk, “Evaluation of reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregate in road bases and subbases,” Transportation Research Record, vol. 1652, pp. 264–269, 1999.
D. Lima, J. Arrieta-Baldovino, and R. L. S. Izzo, “Sustainable use of recycled asphalt pavement in soil stabilization,” Civil Engineering Journal (Iran), vol. 9, no. 9, pp. 2315–2329, 2023, doi: 10.28991/CEJ-2023-09-09-016.
M. M. Hasan, M. R. Islam, and R. A. Tarefder, “Characterization of subgrade soil mixed with recycled asphalt pavement,” Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 207–214, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.jtte.2017.03.007.
J. Suebsuk, A. Suksan, and S. Horpibulsuk, “Strength assessment of cement treated soil–reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) mixture,” International Journal of GEOMATE, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 878–884, 2014, doi: 10.21660/2014.12.3262.
M. Saberian, J. Li, S. T. A. M. Perera, A. Zhou, R. Roychand, and G. Ren, “Large-scale direct shear testing of waste crushed rock reinforced with waste rubber as pavement base/subbase materials,” Transportation Geotechnics, vol. 28, p. 100546, 2021.
S. Perkins, B. Christopher, N. Thom, G. Montestruque, L. Korkiala-Tanttu, and A. Want, “Geosynthetics in pavement reinforcement applications,” in Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Geosynthetics, Guarujá, Brazil, May 23–27, 2010, pp. 1–x.
K. Rajagopal, N. R. Krishnaswamy, and G. Madhavi Latha, “Behaviour of sand confined with single and multiple geocells,” Geotextiles and Geomembranes, vol. 17, pp. 171–184, 1999.
M. G. Shirazi, A. S. A. Rashid, R. Nazir, A. H. Abdul Rashid, and S. Horpibulsuk, “Enhancing the bearing capacity of rigid footing using limited life kenaf geotextile reinforcement,” Journal of Natural Fibers, vol. 17, pp. 1–17, 2020.
H. Alimohammadi, J. Zheng, V. R. Schaefer, J. Siekmeier, and R. Velasquez, “Evaluation of geogrid reinforcement of flexible pavement performance: A review of large-scale laboratory studies,” Transportation Geotechnics, vol. 27, p. 100471, 2021.
S. Mirzapour Mounes, M. R. Karim, A. Khodaii, and M. H. Almasi, “Improving rutting resistance of pavement structures using geosynthetics: An overview,” Scientific World Journal, vol. 2014, p. 764218, 2014.
C. S. Vieira and P. M. Pereira, “Short-term tensile behaviour of three geosynthetics after exposure to recycled construction and demolition materials,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. 273, p. 122031, 2021.
A. Suddeepong, M. Hoy, C. Nuntasena, S. Horpibulsuk, K. Kantatham, and A. Arulrajah, “Evaluation of interface shear strength of natural kenaf geogrid and recycled concrete aggregate for sustainable pavement applications,” Journal of Natural Fibers, vol. 18, no. 10, pp. 1–x, 2021.
M. Korulla, Design Approach for Geogrid Reinforced Flexible Pavement, Public Works Department, 2016. [Online]. Available: https://uppwd.gov.in/site/writereaddata/siteContent/20190424201227766619.pdf
J. P. Gourc and P. Villard, “Reinforcement by membrane effect: Application to embankments on soil liable to subsidence,” in Proc. 2nd Asian Geosynthetics Conf., vol. 1, pp. 55–72, The Institution of Engineers Malaysia, May 2000.
H. Poorahong, P. Jamsawang, N. Thanasisathit, P. Jongpradist, and S. Horpibulsuk, “Enhancing the bearing capacity of unpaved roads on soft clay subgrade using geogrid reinforcement with a triaxial configuration,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 456, p. 139321, 2024.
Y. Liu, Z. Qian, M. Gong, W. Bo, X. Zhang, and C. Xu, “Investigation of the rutting evolution of double-layered heterogeneous asphalt pavement on a steel bridge deck under the coupling of heavy load and variable temperature,” J. Mater. Civ. Eng., vol. 37, no. 7, p. 04025175, 2025.
H. Poorahong, P. Jamsawang, N. Thanasisathit, P. Jongpradist, and G. Jing, “Performance of a triaxial geogrid-reinforced crushed rock base underlain by a soft clay subgrade,” Case Stud. Constr. Mater., vol. 20, p. e03198, 2024.
S. Ahmad, T. Peng, H. Ayaz, and Y. Wu, “Improving geotechnical properties of expansive subgrade using sugar cane molasses and cement,” Appl. Sci., vol. 14, no. 20, p. 9489, 2024.
S. P. Banne, A. W. Dhawale, and S. Pathak, “Influence of wall friction on active earth pressure in model test,” J. Geotech. Eng., 2023. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.37591/joge.v8i1.4421
S. Reehana and M. Muthukumar, “Undrained response of fibre reinforced expansive soil subjected to cyclic loading,” Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng., vol. 173, p. 108154, 2023.
H. Fatehi, S. M. Abtahi, H. Hashemolhosseini, and S. M. Hejazi, “A novel study on using protein-based biopolymers in soil strengthening,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 167, pp. 813–821, 2018.
D. H. Marx, K. Kumar, and J. G. Zornberg, “Quantification of geogrid lateral restraint using transparent sand and deep learning-based image segmentation,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 53–69, 2023.
M. Zhang, H. Zhu, J. Yang, C. Qiu, and A. A. Javadi, “Experimental study of a 3D printed geogrid embedded with FBG sensor for reinforcement of subgrade with underlying cave,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 81–92, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2023.05.001
I. E. Kilic, C. Cengiz, A. Edincliler, and E. Guler, “Seismic behavior of geosynthetic-reinforced retaining walls backfilled with cohesive soil,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 49, no. 5, pp. 1256–1269, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2021.04.004.
W. Zhang, J. F. Chen, and Y. Yu, “Influence of toe restraint conditions on performance of geosynthetic-reinforced soil retaining walls using centrifuge model tests,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 653–661, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2019.103469.
P. Mandhaniya, J. T. Shahu, and S. Chandra, “Numerical analysis on combinations of geosynthetically reinforced earth foundations for high-speed rail transportation,” Structures, vol. 43, pp. 738–751, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2022.07.003.
S. Chawla and J. T. Shahu, “Reinforcement and mud-pumping benefits of geosynthetics in railway tracks: Model tests,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 366–380, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2016.01.005.
Y. S. Jang, B. Kim, and J. W. Lee, “Evaluation of discharge capacity of geosynthetic drains for potential use in tunnels,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 228–239, 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2015.03.001.
D. Robertson, “The oxidative resistance of polymeric geosynthetic barriers (GBR-P) used for road and railway tunnels,” Polym. Test., vol. 32, no. 8, pp. 1594–1602, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.09.012.
C. Jones, Earth Reinforcement and Soil Structures. London, U.K.: Thomas Telford; ASCE Press, 1996.
B. R. Christopher, D. Leshchinsky, and R. Stulgis, “Geosynthetic-reinforced soil walls and slopes: U.S. perspective,” in Proc. Geo-Frontiers Congr., vol. 12, Austin, TX, USA, Jan. 24–26, 2005.
P. Oskouie, B. Becerik-Gerber, and L. Soibelman, “Automated measurement of highway retaining wall displacements using terrestrial laser scanners,” Autom. Constr., vol. 65, pp. 86–101, 2016.
P. D. Coduto, Foundation Design: Principles and Practices, 2nd ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Prentice Hall, 2001, p. 738.
C. S. Desai and K. E. El-Hoseiny, “Prediction of field behavior of reinforced soil wall using advanced constitutive model,” J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng., vol. 131, pp. 729–739, 2005.
V. Elias, B. R. Christopher, and R. R. Berg, Mechanically Stabilized Earth Walls and Reinforced Soil Slopes: Design and Construction Guidelines, 1st ed. Washington, DC, USA: U.S. Dept. Transp., pp. 1–394, 2001.
P. Anderson, R. Gladstone, and J. Sankey, “State of the practice of MSE wall design for highway structures,” in Geotechnical Engineering State of the Art and Practice, pp. 1–21, 2012, doi: 10.1061/9780784412138.0018.
R. Berg, B. Christopher, and N. Samtani, Design and Construction of Mechanically Stabilized Earth Walls and Reinforced Soil Slopes – Volume I. Washington, DC, USA: Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), 2009.
A. Soleimanbeigi and T. Edil, “Compressibility of recycled materials for use as highway embankment fill,” Geotech. Test. J., vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 1–14, 2015, doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001285.
B. Das, Principles of Foundation Engineering, 7th ed. Boston, MA, USA: Cengage Learning, 2007, pp. 406–436.
R. Koerner, Designing with Geosynthetics, 3rd ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Prentice Hall, 1994.
R. Koerner, Designing with Geosynthetics, 5th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Prentice Hall, 2005.
Q. S. Banyhussan and B. A. Hamad, “Investigation of shear strength of subbase–subgrade interface with geosynthetics reinforcement utilizing a large-scale direct shear test,” in E3S Web Conf., vol. 427, p. 03007, 2023, doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202342703007.
K. Halder and D. Chakraborty, “Effect of interface friction angle between soil and reinforcement on bearing capacity of strip footing placed on reinforced slope,” Int. J. Geomech., vol. 19, no. 5, p. 06019008, 2019.
C. Lackner, D. T. Bergado, and S. Semprich, “Prestressed reinforced soil by geosynthetics: Concept and experimental investigations,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 37, pp. 109–123, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2013.02.002.
K. Fabian and A. Fourie, “Performance of geotextile-reinforced clay samples in undrained triaxial tests,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 53–63, 1986.
M. R. Abdi and M. A. Arjomand, “Pullout tests conducted on clay reinforced with geogrid encapsulated in thin layers of sand,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 588–595, 2011.
A. Jotisankasa and N. Rurgchaisri, “Shear strength of interfaces between unsaturated soils and composite geotextile with polyester yarn reinforcement,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 338–353, 2018.
A. Udomchai, M. Hoy, A. Suddeepong, A. Phuangsombat, S. Horpibulsuk, A. Arulrajah, and N. C. Thanh, “Generalized interface shear strength equation for recycled materials reinforced with geogrids,” Sustainability, vol. 13, no. 16, p. 9446, 2021.
J. Stacho, M. Sulovska, and I. Slavik, “Analysis of the shear strength of a soil-geosynthetic interface,” Civil and Environmental Engineering, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 452–463, 2023.
A. Liangsunthonsit, P. Jaroonrat, J. Ayawanna, W. Naebpetch, and S. Chaiyaput, “Evaluation of interface shear strength coefficient of alternative geogrid made from para rubber sheet,” Polymers, vol. 15, no. 7, p. 1707, 2023.
D. H. Marx, K. Kumar, and J. G. Zornberg, “Quantification of geogrid lateral restraint using transparent sand and deep learning-based image segmentation,” Geotext. Geomembr., vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 53–69, 2023.
A. Suddeepong, M. Hoy, C. Nuntasena, S. Horpibulsuk, K. Kantatham, and A. Arulrajah, “Evaluation of interface shear strength of natural kenaf geogrid and recycled concrete aggregate for sustainable pavement applications,” J. Nat. Fibers, vol. 19, no. 13, pp. 6165–6181, 2022.
M. Zhang, X. Ruan, and L. Jiang, “Experimental study on cyclic shear performance of the four-way geogrid reinforcement–soil interface,” Appl. Sci., vol. 14, no. 4, p. 1373, 2024.
S. Adhikari, M. J. Khattak, and B. Adhikari, “Mechanical characteristics of soil-RAP-geopolymer mixtures for road base and subbase layers,” Int. J. Pavement Eng., vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 483–496, 2020, doi: 10.1080/10298436.2018.1492131.
K. Sweta and S. K. K. Hussaini, “Performance of the geogrid-reinforced railroad ballast in direct shear mode,” Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. – Ground Improv., vol. 172, no. 4, pp. 244–256, 2019.
A. Suddeepong, N. Sari, S. Horpibulsuk, A. Chinkulkijniwat, and A. Arulrajah, “Interface shear behaviours between recycled concrete aggregate and geogrids for pavement applications,” Int. J. Pavement Eng., vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 228–235, 2020.
M. Kang, J. H. Kim, I. I. Qamhia, E. Tutumluer, and M. H. Wayne, “Geogrid stabilization of unbound aggregates evaluated through bender element shear wave measurement in repeated load triaxial testing,” Transp. Res. Rec., vol. 2674, no. 3, pp. 113–125, 2020.
L. Xu, R. Wang, D. Xu, J. Wang, X. Wang, and Q. Meng, “Interface shear behavior of geogrid-reinforced calcareous sand under large-scale monotonic direct shear,” Int. J. Geosynthetics Ground Eng., vol. 8, no. 5, p. 66, 2022.
S. Sarkar and A. Hegde, “Performance evaluation of geogrid reinforced recycled marginal backfill materials in triaxial test conditions,” Int. J. Geosynthetics Ground Eng., vol. 8, no. 4, p. 48, 2022.
R. Anda, L. Wang, M. J. Ying, and Y. T. Huang, “Analysis of shear characteristics of recycled concrete aggregate–geogrid interface,” J. Mater. Civ. Eng., vol. 35, no. 7, p. 04023169, 2023.
K. Shireen, R. M. Varghese, and N. Sankar, “Shear strength characteristics of bottom ash–rubber mixture reinforced with geogrids,” Int. J. Geosynthetics Ground Eng., vol. 9, no. 1, p. 7, 2023.
S. Maramizonouz, S. Nadimi, W. Skipper, and R. Lewis, “Characterisation and tribological testing of recycled crushed glass as an alternative rail sand,” Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part F: J. Rail Rapid Transit, vol. 237, no. 10, pp. 1353–1358, 2023.
F. L. Liu, K. J. Kong, and J. Yao, “Effects of rock content and degree of compaction on interface shear characteristics of geogrid-soil-rock mixture,” Chin. J. Geotech. Eng., vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 903–911, 2023.
B. Ok, H. Colakoglu, and U. Dagli, “Evaluation of the geogrid-various sustainable geomaterials interaction by direct shear tests,” Geomech. Eng., vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 173–186, 2023.
M. A. M. Al-Dulaimi, “Numerical analysis of geogrids and recycled concrete aggregate for stabilizing road embankments,” Ann. Chim. Sci. Mater., vol. 47, no. 4, p. 219, Aug. 2023.
M. N. Alam and S. K. K. Hussaini, “Performance of geogrid-reinforced rubber-coated ballast and natural ballast mix under direct shear conditions,” J. Mater. Civ. Eng., vol. 35, no. 9, p. 04023290, 2023.
C. H. Ho, J. DeGeyter, and D. Zhang, “Five-year performance evaluation of geogrid reinforcement in low-volume unpaved roads using dynamic cone penetrometer, plate load test and roadway sensing,” Geotechnics, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 306–319, 2023.
T. A. N. Peng, L. I. Hai, L. I. Xiangping, G. U. Fan, and J. H. Zhang, “Experimental study on reinforced geogrid of construction and demolition wastes based on DIC technology,” J. China & Foreign Highway, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 1–10, 2024.