Influence of Nano-TiO₂ Additives on the Swelling Behavior of Expansive Soils
Main Article Content
Abstract
Expansive soils, rich in clay minerals, undergo significant swelling and shrinkage with moisture changes, often damaging foundations and infrastructure. To mitigate these challenges, ground improvement is essential, commonly achieved through chemical or physical stabilization methods.
Nanomaterials have recently emerged as promising stabilizing agents in geotechnical engineering. Their use bridges civil engineering, material science, and nanotechnology. Incorporating nanomaterials to reduce soil swelling is gaining attention as an innovative improvement technique.
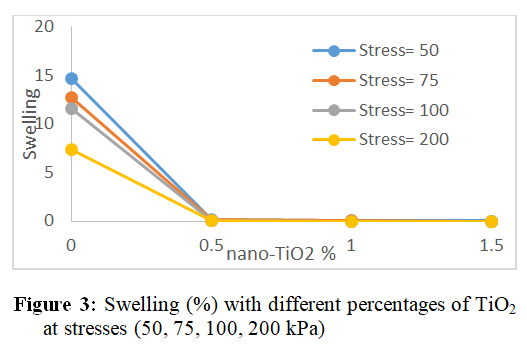
This study presents an experimental investigation into the effect of Titanium dioxide (TiO2) on the swelling behavior of expansive soil. TiO2 were added at three different dosages (0.5%, 1.0%, and 1.5%) by dry weight of soil. The swelling characteristics of the natural expansive soil were first evaluated in its untreated condition, followed by an assessment of the influence of TiO2 through a series of one-dimensional odometer swell tests.
Swelling tests were conducted under a range of vertical pressures (50, 75, 100, 200, and 400 kPa) to quantify the changes in swell percentages and swelling pressure due to TiO2 treatment. The results contribute to a better understanding of the potential of nanomaterials, particularly TiO2, in mitigating the adverse effects of expansive soils in geotechnical applications.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Licensed under a CC-BY license: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
How to Cite
References
Estabragh AR, Parsaei B, Javadi AA (2015) Laboratory investigation of the effect of cyclic wetting and drying on the behavior of an expansive soil. Soils Found 55(2):304–314
A. Tabarsa, N. Latifi, C. L. Meehan, and K. N. Manahiloh, "Laboratory investigation and field evaluation of loess improvement using nanoclay–A sustainable material for construction," Construction and Building Materials, vol. 158, pp. 454-463, 2018.
N. Ghasabkolaei, A. J. Choobbasti, N. Roshan, and S. E. Ghasemi, "Geotechnical properties of the soils modified with nanomaterials: A comprehensive review," Archives of civil and mechanical engineering, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 639-650, 2017.
S. H. Bahmani, N. Farzadnia, A. Asadi, and B. B. Huat, "The effect of size and replacement content of nanosilica on strength development of cement treated residual soil," Construction and Building Materials, vol. 118, pp. 294-306, 2016.
G. Omidi, T. Prasad, J. Thomas, and K. Brown, "The influence of amendments on the volumetric shrinkage and integrity of compacted clay soils used in landfill liners," Water, air, and soil pollution, vol. 86, no. 1, pp. 263-274, 1996.
Odeh, N. A., & Al-Rkaby, A. H. (2022). Strength, Durability, and Microstructures characterization of sustainable geopolymer improved clayey soil. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 16, e00988..
B. Z. Mahasneh, "Assessment of using cement, Dead Sea sand and oil shale in treating soft clay soil," European Journal of Scientific Research, vol. 128, no. 4, pp. 245-255, 2015.
J. Nelson and D. J. Miller, Expansive soils: problems and practice in foundation and pavement engineering. John Wiley & Sons, 1997.
Djellali A, Houam A, Saghafi B (2017) Indirect estimation of swelling pressure of clayey subgrade under pavement structures. Arab J Sci Eng 42:3991–3999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2842-2
Masin D (2017) Coupled thermohydromechanical double-structure model for expansive soils. J Eng Mech 143:3442–3455. https://doi.org/ 10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001376
NATIONAL NANOTECHNOLOGY INITIATIVE," 2007.
NSTC (2007) The National Nanotechnology Initiative—Strategic Plan, December 2007. Executive Office of the President of the United States
G. Finch et al., "Nanomedicine drug development: A scientific symposium entitled “Charting a roadmap to commercialization”," The AAPS journal, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 698-704, 2014.
I. Mugica, C. Fito, M. Domat, P. Dohanyosova, C. Gutierrez-Canas, and S. Lopez-Vidal, "Novel techniques for detection and characterization of nanomaterials based on aerosol science supporting environmental applications," Science of the Total Environment, vol. 609, pp. 348-359, 2017.
Kim C-S, Cho K, Manjili MH et al (2017) Mechanical performance of particulate-reinforced Al metal-matrix composites (MMCs) and Al metal-matrix nano-composites (MMNCs). J Mater Sci 52:13319– 13349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1827-6
Audichon T, Guenot B, Baranton S et al (2017) Effect of the annealing atmosphere on the electrochemical properties of RuO2 nano-oxided synthesized by the Instant Method. Appl Catal B Environ 218:385–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.027
Viana M, Fonseca AS, Querol X et al (2017) Workplace exposure and release of ultrafine particles during atmospheric plasma spraying in the ceramic industry. Sci Total Environ 599:2065–2073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.253
Indira K, Nishimura T (2017) In-situ electrochemical monitoring and ex- situ chemical analysis of epoxy coated steels in sodium chloride environment using various spectroscopic techniques. Trans Indian Inst Metals 70:2347–2360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017- 1135-5
Yu Huang, Lin Wang (2016) Experimental studies on nanomaterials for soil improvement.
J. He, D. Wang, and D. Zhou, "Transport and retention of silver nanoparticles in soil: Effects of input concentration, particle size and surface coating," Science of the Total Environment, vol. 648, pp. 102-108, 2019.
Gulati, S., Sachdeva, M., & Bhasin, K. K. (2018, May). Various synthetic routes for the preparation of nanoparticles. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 1953, No. 1, p. 030215). AIP Publishing LLC.
Reddy, P. S., Yang, Y. L., Mohanty, B., & Rao, B. H. (2022). Assessment of testing method influence on swelling characteristics of expansive soils of India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 15(12), 1132.
Sharma, R., Sarkar, A., Jha, R., Kumar Sharma, A., & Sharma, D. (2020). Sol‐gel–mediated synthesis of TiO2 nanocrystals: Structural, optical, and electrochemical properties. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 17(3), 1400-1409.
Yin, H., Zhang, L., & Xie, X. (2018). Effect of TiO₂ nanoparticles on the compaction characteristics of clayey soil. Applied Clay Science, 153, 47-55.
Rashad, A. M., El-Didamony, H., & Abd El-Rahman, S. (2020). Soil stabilization with TiO₂ nanoparticles: Improvement of strength and durability. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 43(4), 839-854.