Walnut Shells as Sustainable Low-Cost Adsorbents for the Removal of Cadmium and Nickel from Aqueous Solutions
Main Article Content
Abstract
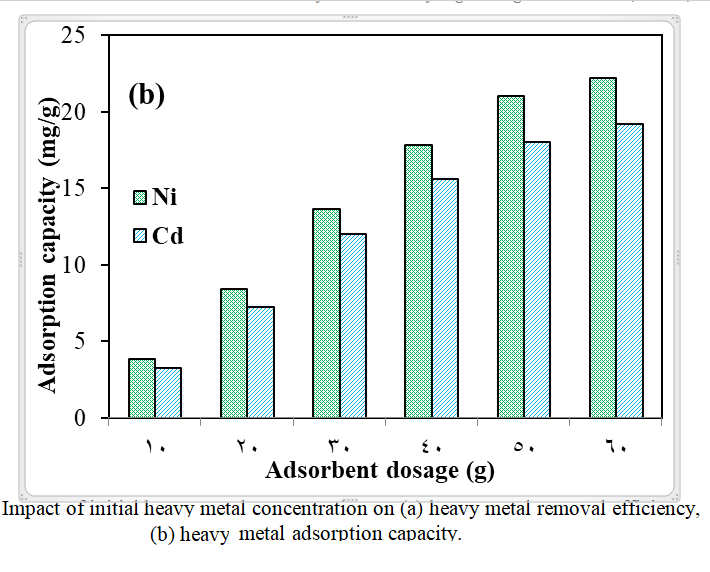
The rapid development of industries has led to increased release of heavy metals into the environment. When released into the environment, metals have a tendency to linger eternally, build up in living tissues across the food chain, and endanger both the ecosystem and public health. Usually present in trace amounts in industrial wastewater, heavy metals are difficult to remove from water. In the current study, an adsorbent composed of walnut shells waste powder was manufactured and tested for the adsorption of heavy metals cadmium (Cd) and nickel (Ni) from synthetic aqueous solution. Several experimental conditions affecting the removal process were controlled, including pH, contact time, adsorbent dosage, temperature of solution, and initial concentration of Cd and Ni, to achieve optimal removal conditions. The adsorption technique was effectively implemented, attaining, under ideal circumstances, a removal efficiency of 95% for Cd and 99% for Ni. Additionally, the adsorption capacity (qe) of 14.25 mg/L for Cd and 14.85 mg/g for Ni. The optimum conditions for removing heavy metals (Cd and Ni) were: The initial metal concentrations are 30 mg/L, the bioadsorbent dosage is 2 g/L, the adsorbent particle size is between 0.3 and 0.075 mm, the agitation speed is 150 rpm, the contact period is 60 minutes, the pH is 5, and the solution temperature is 45°C. In summary, this study's suggested walnut shell material offers an economical, ecologically responsible, and alternative adsorbent for removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions by adsorption.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Licensed under a CC-BY license: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
How to Cite
References
E. Q. Shehab and R. Alsultani, “A new approach to sustainable environmental assessment for wastewater treatment plants-A case study in the central region of Iraq.,” Ecological Engineering & Environmental Technology (EEET), vol. 26, no. 1, 2025.
M. Ullah et al., “The effective removal of heavy metals from water by activated carbon adsorbents of Albizia lebbeck and Melia azedarach seed shells.,” Soil & Water Research, vol. 15, no. 1, 2020.
A. H. Khalaf, Q. A. Ali, H. S. Alhares, H. H. Abd-Almohi, S. J. Mohammed, and M. F. Murshed, “Removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solutions by centrifugation using activated carbon from Ficus benjamina as an adsorbent,” Int J Environ Anal Chem, pp. 1–30, 2025.
S. J. Mohammed, M. J. M-Ridha, K. M. Abed, and A. A. M. Elgharbawy, “Removal of levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions and an economic evaluation using the electrocoagulation process,” Int J Environ Anal Chem, vol. 103, no. 16, pp. 3801–3819, Dec. 2023, doi: 10.1080/03067319.2021.1913733.
R. R. Al-Ani, A. Al Obaidy, and R. M. Badri, “Assessment of water quality in the selected sites on the Tigris River, Baghdad-Iraq,” Int J Adv Res (Indore), vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 1125–1131, 2014.
M. F. Ali, Q. A. Ali, M. J. M-Ridha, S. J. Mohammed, and H. R. Bohan, “Phytoremediation of tetracycline via the coontail Ceratophyllum demersum in antibiotics-contaminated water,” Biocatal Agric Biotechnol, vol. 53, Oct. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2023.102887.
S. T. Jawed and A. F. Shihab, “The Effect of Heavy Water Waste on the Euphrates River in Increasing the Concentration of Some Heavy Metals,” Procedia of Engineering and Life Science, vol. 5, pp. 745–754, 2024.
S. J. Mohammed, M. J. MRidha, Q. A. Ali, K. M. Abed, and S. Ahmadzadeh, “Reliable treatment approach for levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin removal from aqueous medium: process modelling, kinetic and isotherm studies,” Desalination Water Treat, vol. 307, pp. 50–62, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.5004/dwt.2023.29776.
G. M. Aziz et al., “Activity of laccase enzyme extracted from Malva parviflora and its potential for degradation of reactive dyes in aqueous solution,” Biocatal Agric Biotechnol, vol. 50, Jul. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2023.102671.
J. S. Piccin, C. S. Gomes, B. Mella, and M. Gutterres, “Color removal from real leather dyeing effluent using tannery waste as an adsorbent,” J Environ Chem Eng, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1061–1067, Mar. 2016, doi: 10.1016/J.JECE.2016.01.010.
M. J. M-Ridha et al., “Subsurface Flow Phytoremediation Using Barley Plants for Water Recovery from Kerosene-Contaminated Water: Effect of Kerosene Concentration and Removal Kinetics,” Water (Switzerland), vol. 14, no. 5, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.3390/w14050687.
P. C. Nagajyoti, K. D. Lee, and T. V. M. Sreekanth, “Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review,” Environ Chem Lett, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 199–216, 2010.
Q. Manzoor, R. Nadeem, M. Iqbal, R. Saeed, and T. M. Ansari, “Organic acids pretreatment effect on Rosa bourbonia phyto-biomass for removal of Pb (II) and Cu (II) from aqueous media,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 132, pp. 446–452, 2013.
M. J. M-Ridha, S. L. Zeki, S. J. Mohammed, K. M. Abed, and H. A. Hasan, “Heavy Metals Removal from Simulated Wastewater using Horizontal Subsurface Constructed Wetland,” Journal of Ecological Engineering, vol. 22, no. 8, pp. 243–250, 2021.
C. K. Jain, D. S. Malik, and A. K. Yadav, “Applicability of plant based biosorbents in the removal of heavy metals: a review,” Environmental Processes, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 495–523, 2016.
G. Özsin, M. Kılıç, E. Apaydın-Varol, and A. E. Pütün, “Chemically activated carbon production from agricultural waste of chickpea and its application for heavy metal adsorption: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies,” Appl Water Sci, vol. 9, no. 3, p. 56, 2019.
C. Duan, T. Ma, J. Wang, and Y. Zhou, “Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using carbon-based adsorbents: A review,” Journal of Water Process Engineering, vol. 37, p. 101339, 2020.
H. A. Alalwan, M. A. Kadhom, and A. H. Alminshid, “Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using agricultural byproducts,” Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology—AQUA, vol. 69, no. 2, pp. 99–112, 2020.
K. K. Mar, D. Karnawati, D. P. E. Putra, T. Igarashi, and C. B. Tabelin, “Comparison of Arsenic adsorption on lignite, bentonite, shale, and iron sand from Indonesia,” Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, vol. 6, pp. 242–250, 2013.
Q. A. Ali, M. F. Ali, S. J. Mohammed, and M. J. M-Ridha, “Utilising date palm fibres as a permeable reactive barrier to remove methylene blue dye from groundwater: a batch and continuous adsorption study,” Environ Monit Assess, vol. 196, no. 11, p. 1112, 2024.
M. S. Salman, H. S. Alhares, Q. A. Ali, M. J. M-Ridha, S. J. Mohammed, and K. M. Abed, “Cladophora Algae Modified with CuO Nanoparticles for Tetracycline Removal from Aqueous Solutions,” Water Air Soil Pollut, vol. 233, no. 8, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11270-022-05813-4.
I. Uzun, “Kinetics of the adsorption of reactive dyes by chitosan,” Dyes and pigments, vol. 70, no. 2, pp. 76–83, 2006.
H. S. Alhares et al., “Rice husk coated with copper oxide nanoparticles for 17α-ethinylestradiol removal from an aqueous solution: adsorption mechanisms and kinetics,” Environ Monit Assess, vol. 195, no. 9, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.1007/s10661-023-11689-6.
P. N. Omo-Okoro, A. P. Daso, and J. O. Okonkwo, “A review of the application of agricultural wastes as precursor materials for the adsorption of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: A focus on current approaches and methodologies,” Environ Technol Innov, vol. 9, pp. 100–114, 2018.
Q. A. Ali et al., “Date Palm Fibre Waste Exploitation for the Adsorption of Congo Red Dye via Batch and Continuous Modes,” Journal of Ecological Engineering, vol. 24, no. 10, pp. 259–276, 2023, doi: 10.12911/22998993/169176.
M. A. Ibrahim et al., “Simultaneous Adsorption of Ternary Antibiotics (Levofloxacin, Meropenem, and Tetracycline) by SunFlower Husk Coated with Copper Oxide Nanoparticles,” Journal of Ecological Engineering, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 30–42, 2022.
H. S. Alhares et al., “Sunflower Husks Coated with Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Reactive Blue 49 and Reactive Red 195 Removals: Adsorption Mechanisms, Thermodynamic, Kinetic, and Isotherm Studies,” Water Air Soil Pollut, vol. 234, no. 1, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1007/s11270-022-06033-6.
G. Liu, L. Zhang, and R. Luo, “Preparation of efficient heavy metal adsorbent based on walnut shell and adsorption for Pb (II) ions from aqueous solution,” Springer, vol. 29, no. 18, pp. 9819–9830, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.1007/S10570-022-04869-Z.
V. Halysh et al., “Walnut shells as a potential low-cost lignocellulosic sorbent for dyes and metal ions,” Springer, vol. 25, no. 8, pp. 4729–4742, Aug. 2018, doi: 10.1007/S10570-018-1896-Y.
S. J. Mohammed and M. J. Mohammed-Ridha, “Optimization of Levofloxacin Removal From Aqueous Solution Using Electrocoagulation Process By Response Surface Methodology,” Iraqi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 204–217, Feb. 2021, doi: 10.36103/IJAS.V52I1.1252.
M. Venkata Subbaiah et al., “Adsorption of Reactive Red 195 from aqueous medium using Lotus ( Nelumbo nucifera ) leaf powder chemically modified with dimethylamine: characterization, isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics, and mechanism assessment,” Int J Phytoremediation, vol. 24, pp. 1–14, May 2021, doi: 10.1080/15226514.2021.1929060.
S. Tunali Akar, A. Gorgulu Ari, Z. Pat, B. Anilan, and T. Akar, “Biosorption of Reactive Blue 49 Dye under Batch and Continuous Mode Using a Mixed Biosorbent of Macro-Fungus Agaricus bisporus and Thuja orientalis Cones,” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 148, pp. 26–34, May 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.07.027.
H. Alhares et al., “Sunflower Husks Coated with Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Reactive Blue 49 and Reactive Red 195 Removals: Adsorption Mechanisms, Thermodynamic, Kinetic, and Isotherm Studies,” Water Air Soil Pollut, vol. 234, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1007/s11270-022-06033-6.
K. Akpomie, F. Dawodu, E. Samson, A. Niyi, and J. Ani, “Heavy metal remediation from automobile effluent by thermally treated montmorillonite-rice husk composite,” Transactions of the Royal Society of South Africa, vol. 73, Sep. 2018, doi: 10.1080/0035919X.2018.1518850.
J. S. Raghuwanshi and N. Lal, “Removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution using tea waste as an adsorbent: A comprehensive review,” International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), vol. 5, no. 9, pp. 266–272, 2018.
A. James and D. Yadav, “Valorization of coconut waste for facile treatment of contaminated water: A comprehensive review (2010–2021),” Environ Technol Innov, vol. 24, p. 102075, Nov. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2021.102075.
T. A. Khan, S. Dahiya, and I. Ali, “Use of kaolinite as adsorbent: Equilibrium, dynamics and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution,” Appl Clay Sci, vol. 69, pp. 58–66, 2012.
R. Srivastava and D. C. Rupainwar, “Eucalyptus bark powder as an effective adsorbent: Evaluation of adsorptive characteristics for various dyes,” Desalination Water Treat, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 302–313, 2009, doi: https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2009.864.